What Could Go Wrong?! 48,500-Year-Old Siberian Virus is Revived
The world’s oldest known frozen and dormant virus has been revived in a French laboratory leading many to express concerns about the dangers of bringing to life ancient microbes. The virus was removed from the Siberian permafrost in Russia’s far east and is 48,500 years old, offering proof that viruses are incredibly hardy and capable of surviving indefinitely when they’re preserved in a frozen state.
Melting Siberian Permafrost in a Virus-Filled Pandora’s Box
This particular virus is actually one of nine different types of viruses that have been resuscitated from Siberian permafrost samples in recent years. That includes seven viruses resuscitated for this new study, and two other approximately 30,000-year-old viruses brought back to life by the same team of researchers from other samples taken in 2013. The youngest of these viruses was frozen 27,000 years ago.
As reported in the non-peer-reviewed journal bioRxiv, the 48,500-year-old virus has been named Pandoravirus yedoma, in reference to Pandora’s box. The virus was found in a sample of permafrost taken from 52 feet (16 m) below the bottom of a lake in Yukechi Alas in the Russian Republic of Yakutia.
- Long Frozen Organisms in the Arctic Awakened, Hinting at Life on Other Planets
- Ancient Mega-Virus That Does Not Resemble Any Virus on Earth is Set to be Revived
The first-ever pandoravirus was one of the two viruses found in 2013, although that one was of a different type altogether. “48,500 years is a world record,” Jean-Michel Claverie, a virologist at Aix-Marseille University in France and the lead author of the permafrost viral study, told the New Scientist.
In addition to its age, the other remarkable feature of this pandoravirus is its size. Classified as a type of giant virus, Pandoravirus yedoma is approximately one micrometer long and .5 micrometers wide. This means they can be examined directly under a microscope. It contains approximately 2,500 genes, in contrast to the miniscule modern viruses that infect humans that possess no more than 10 to 20 genes.
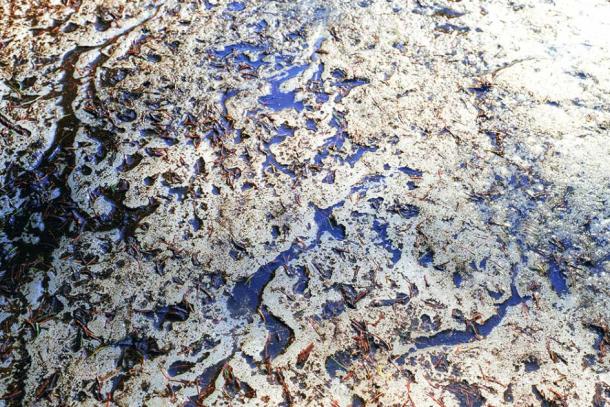

Climate change and the resulting thawing of the permafrost could release a mass of new Siberian viruses into the atmosphere. (Андрей Михайлов / Adobe Stock)
Climate Change and the Threat of Permafrost Viral Release
Given the disturbing coronavirus pandemic the world has just experienced, it might seem alarming that these scientists are intentionally reviving long-lost viruses previously hidden in the frozen wastelands of Siberia. But they say this research is necessary to evaluate the dangers associated with climate change.
“One quarter of the Northern Hemisphere is underlain by permanently frozen ground, referred to as permafrost,” they wrote in their newly published paper. With the thawing of the permafrost, organic matter which has been frozen for as many as a million years is thawing out. One of the effects of this is the release of carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere, amplifying the greenhouse effect.
The other is that “part of this organic matter also consists of revived cellular microbes (prokaryotes, unicellular eukaryotes) as well as viruses that remained dormant since prehistorical times,” explained the authors in bioRxiv. Only by extracting viruses from permafrost samples and reviving them in controlled conditions, the scientists claim, will it be possible to evaluate the nature of the threat they might pose to human health and safety in a warmer, permafrost-free future.
Since permafrost covers more one-fourth of all land territory in the Northern Hemisphere, this is not an idle concern. The viral load currently locked up in permanently frozen ground is undoubtedly massive, and if it were all released over the course of a couple of decades it could conceivably set off an avalanche of new viral infections in a variety of host species.
None of these victims would be immune to the impact of viral agents that had been out of circulation for tens of thousands of years. Immune systems would eventually adjust, but that might happen too late to prevent a catastrophic loss of life that cuts across the microbial-, plant- and animal-life spectrums.
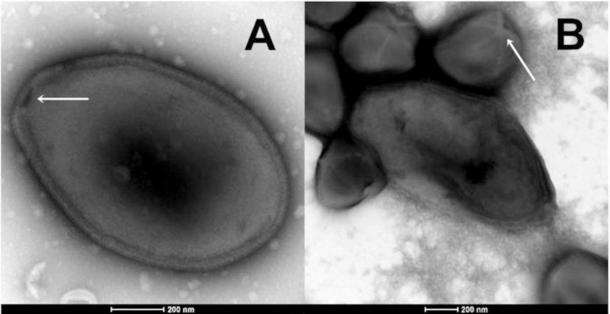
The 48,500-year-old Siberian virus is a pandoravirus, which infects single-cell organisms known as amoebas. (Claverie et. al / bioRxiv)
Immortal Viruses May Be Returning Soon, in Quantities too Astounding to Imagine
Concerns about permafrost melting are not only theoretical. The once-frozen ground has already started to thaw in some areas, and that has allowed scientists to recover frozen and well-preserved specimens of animals that lived during the Paleolithic period.
In recent years the remains of wooly rhinos that went extinct 14,000 years ago have been found, and in one instance scientists recovered a 40,000-year-old wolf’s head that was in almost pristine condition. Wooly mammoth remains have proven especially easy to find in the freshly-thawed soil, so much so that a black-market industry has arisen in which mammoth tusks removed from illicitly unearthed mammoth skeletons are being sold to ivory traders.
What concerns scientists about this development is that potent infectious agents may be hiding dormant inside these well-preserved ancient animal remains. It is notable that the 27,000-year-old virus found in this new study was not removed from the lake bottom sample, but was instead extracted from frozen mammoth excrement taken from a different permafrost core.
Needless to say, ancient viruses released from thawed animal hosts would be more likely to evolve into something threatening to humans than a virus that specifically attacks microbes like amoeba.

Winter landscape and frozen lake in Yakutia, Siberia. (Tatiana Gasich / Adobe Stock)
The Hidden Danger of Ancient Bacteria and Viruses in the Thawing Permafrost
In their research paper, Professor Claverie and his colleagues emphasized how dangerous ancient bacteria and viruses could be to present-day life forms of all types. Even if frozen in deeper levels of permafrost for millions of years, they could become active again should the permafrost disappear.
In comparison to outbreaks from modern viruses, “the situation would be much more disastrous in the case of plant, animal, or human diseases caused by the revival of an ancient unknown virus,” the French scientists wrote. “As unfortunately well documented by recent (and ongoing) pandemics, each new virus, even related to known families, almost always requires the development of highly specific medical responses, such as new antivirals or vaccines.”
The Arctic regions of the planet are largely free of permanent human settlers. But the researchers point out that more people are visiting the planet’s coldest regions than ever before, mainly to harvest valuable resources like oil, gold and diamonds that are present in abundance in these previously under-explored areas. In strip-mining operations the upper layers of the permafrost are actually torn out intentionally, meaning that viral exposures during such operations may be unavoidable.
- Ancient Diseases Released By Rapid Permafrost Meltdown Threaten Europe
- Cryogenic Breakthrough: Worms Frozen in Permafrost for 42,000 Years Have Been Resuscitated!
“How long these viruses could remain infectious once exposed to outdoor conditions (UV light, oxygen, heat), and how likely they will be to encounter and infect a suitable host in the interval, is yet impossible to estimate,” the scientists concluded. “But the risk is bound to increase in the context of global warming when permafrost thawing will keep accelerating, and more people will be populating the Arctic in the wake of industrial ventures.”
Other scientists have warned of the dangers of viruses being released in the Arctic through the melting of glaciers, which is yet another possible side effect of global warming. This could expose animals and humans to flowing rivers of glacial meltwater that could carry pathogens to new areas further south.
Whether any of these worst-case scenarios come to fruition remains to be seen. But even a small amount of melting, regardless of the cause, could be enough to release some potentially hazardous viral agents into the global environment, where billions of vulnerable people live.
Top image: Colony of microbes, representational image. Source: iarhei / Adobe Stock
By Nathan Falde

















Comments
https://www.inverse.com/article/49747-what-is-the-human-virome
The natural warming period corresponding to most of the latter half of the 20th century is well-and-truly over. It is now cooling just as naturally.
Junk scientists and the even junkier media are the real virus and what unthaws them is money and lots of it. The fact is that there are many people who get paid to not tell the truth and no amount of ignoring it will make that situation go away.
This article is pure fear porn. Just another one of many to generate a culture of fear. I am beggining to think that there is a massive umbrella controlling the media and some are paid to generate fear in the populace.
"Only by extracting viruses from permafrost samples and reviving them in controlled conditions, the scientists claim, will it be possible to evaluate the nature of the threat they might pose to human health"
This is rubbish, one cannot evaluate the effect by analysing the particle. (virus, if you will).
"capable of surviving indefinitely"
How can something which is not alive, survive.
Does this make me question the remainder of the article.
The term ‘live Virus’ means only those created from living tissue cultures in vitro.
‘Live Virus’ in medical terminology does not mean that the Virus is actually alive, in the sense that we understand.
They are not in themselves ‘alive’, except being molecules of DNA and protein.
If they have no life then the words ‘dead’ Virus’ cannot be an applicable phrase but it is used fluidly by the medical profession.
Pages