Did Ancient Japanese Fishermen Reach South America 5,000-Years-Ago?
The notion that pre-Columbian cultures from Europe, Africa, or Asia sailed across the Atlantic and Pacific oceans to discover America, is a popular theory backed by numerous books and television documentaries. While most of these claims seem baseless, one theory did gain some credibility, in that it was backed by a reputable archaeologist from the esteemed Smithsonian Institution, the so-called ‘Jōmon-Valdivia hypothesis’. Until recently, mainstream historians and archaeologists most often shunned ideas about ancient transcontinental oceanic travel and the entire notion was considered as pseudoscience. Even in the face of new findings around the world that support the idea that oceans were travelled by ancient peoples who had both the motivation, and means to do so, many archaeologists still refuse to engage with the term “ancient transoceanic voyage.” And this is not as dogmatic as one might at first think, for the history of the subject is infected with mistakes, misinterpretations, and hoaxes that have left trails of confusion in their wake.
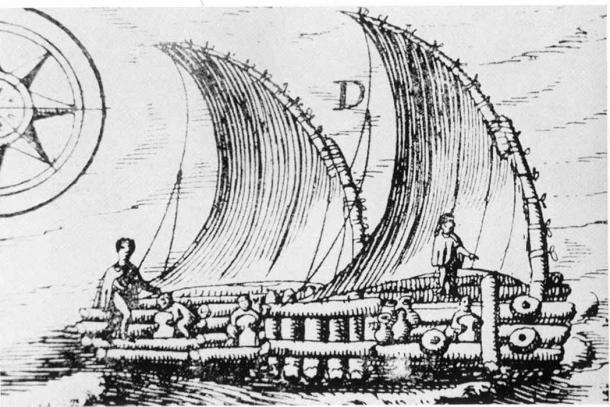
A drawing of a raft (balsa) near Guayaquil, Ecuador in 1748. The drawing resembles the description given by 16th-century Spanish explorers of the rafts used by Indians. (Public Domain)
Some theorists suggest that the lost tribes from Israel appeared in North America, or that Phoenicians made it to Lake Titicaca in Bolivia, but no one story has left such a wake of confusion as the ‘Jōmon-Valdivia hypothesis’, a 50-year long archaeological delusion that suggested the ancient peoples of Ecuador did not develop their own culture, but that they inherited it from prehistoric fishermen from Japan around 3000 BC.
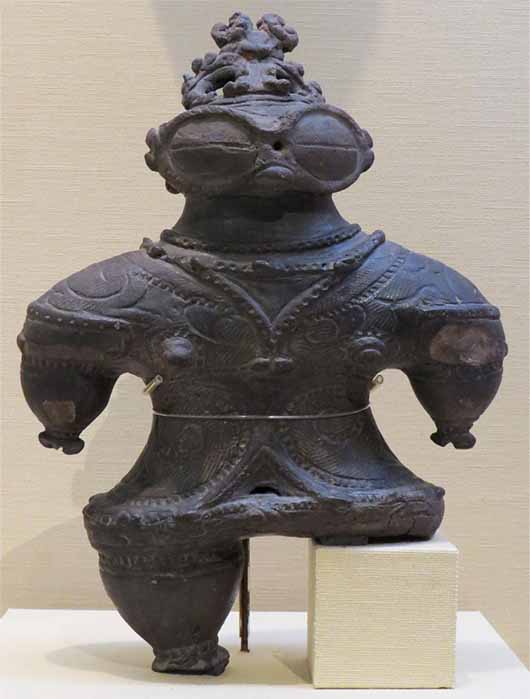

Final Jōmon dogū (土偶) earthenware figure (c. 1000 - 400 BC) (CC BY-SA 4.0)
The Jōmon period in Japanese history extended from circa 14,000–300 BC and represents an epoch when diverse hunter-gatherer groups merged with early agriculturalists through a common Jōmon culture. The name ‘Jōmon’ means cord-marked, referring to the twisted cord impressions that decorate the iconic pottery from this time, which is generally accepted to be among the oldest decorated clay crafts in the world. The earliest pottery fragments in Japan were found at the Odai Yamamoto I site in 1998 and date back to 14,500 BC, and similarly dated pottery was later recovered from the Kamikuroiwa archaeological site, and from within the Fukui cave.
Like this Preview and want to read on? You can! JOIN US THERE ( with easy, instant access ) and see what you’re missing!! All Premium articles are available in full, with immediate access.
For the price of a cup of coffee, you get this and all the other great benefits at Ancient Origins Premium. And - each time you support AO Premium, you support independent thought and writing.
Ashley Cowie is a Scottish historian, author and documentary filmmaker presenting original perspectives on historical problems, in accessible and exciting ways. His books, articles and television shows explore lost cultures and kingdoms, ancient crafts and artifacts, symbols and architecture, myths and legends telling thought-provoking stories which together offer insights into our shared social history. www.ashleycowie.com.
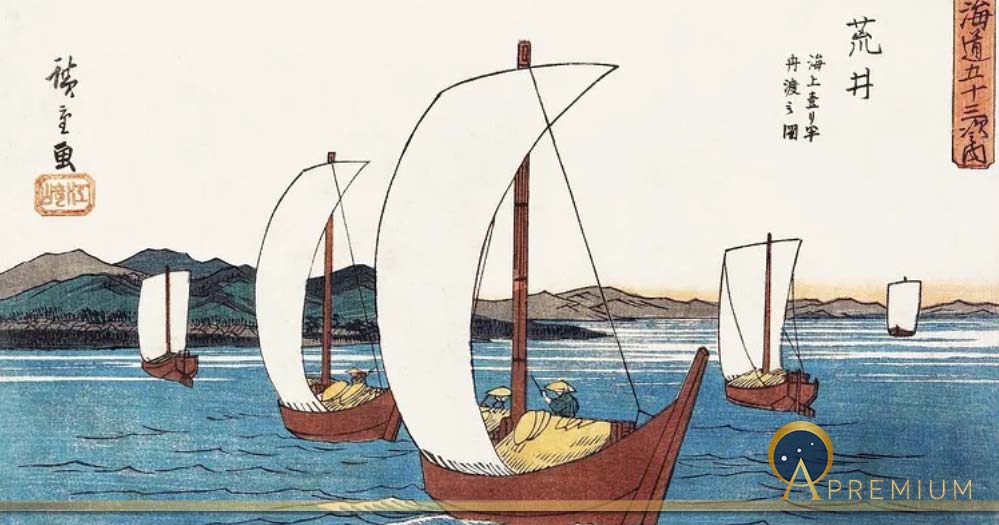
Top Image: Utagawa Hiroshige's Sailing Boats at Arai (Public Domain)
By: Ashley Cowie



















